1、引言
在当今数字化时代,网络安全已成为企业和个人用户关注的焦点。IP 黑白名单作为一种有效的网络安全策略,允许我们精确控制对 Web 资源的访问权限。通过白名单,我们可以确保只有可信的 IP 地址能够访问敏感资源;而黑名单则可以阻止恶意 IP 的访问,从而减少安全风险。
选择 Nginx OpenResty 与 Redis 作为实现黑白名单的解决方案,是基于以下几个原因:
- 高性能:Nginx 以其轻量级和高性能著称,适合处理高并发请求。
- 灵活性:OpenResty 通过集成 Lua 脚本,提供了强大的定制能力。
- 可扩展性:Redis 作为一个内存数据结构存储,支持数据的快速读写,适合实现动态的黑白名单管理。
2、简介
1、什么是 OpenResty?
OpenResty 是一个基于 Nginx 的全功能 Web 平台,它集成了一系列精心设计的 Lua 库、第三方模块和一个基于 LuaJIT 的轻量级 Web 框架。OpenResty 的核心是 Nginx,但它通过 Lua 语言扩展了 Nginx 的功能,使其能够构建能够处理超高并发的动态 Web 应用。
2、OpenResty 与 Nginx 的关系
OpenResty 是在 Nginx 的基础上构建的,它保留了 Nginx 的所有功能,并通过 Lua 语言扩展了其能力。这意味着你可以使用 OpenResty 来实现 Nginx 的所有功能,同时还能够利用 Lua 脚本来实现更复杂的业务逻辑。
3、环境安装
1、环境版本
centos 7
redis 7.2
nginx version: openresty/1.25.3.1
2、环境安装
1、添加 OpenResty 仓库
# 由于公共库中找不到openresty,所以需要添加openresty的源仓库
yum-config-manager --add-repo https://openresty.org/package/centos/openresty.repo
# 注意,如果上面命令提示不存在,那就先安装一下
yum install -y yum-utils
- 安装 OpenResty
# 安装openresty
yum install -y openresty
# 安装OpenResty管理工具,帮助我们安装第三方的Lua模块
yum install -y openresty-opm
3、目录结构
默认安装在 / usr/local/openresty
看到里面有一个 nginx 目录,进去可以看到跟我们平常用的 nginx 是一模一样的,OpenResty 就是在 Nginx 基础上集成了一些 Lua 模块
到这里我们就安装好了
4、启动和运行
OpenResty 底层是基于 Nginx 的,查看 OpenResty 目录的 nginx 目录,结构与 windows 中安装的 nginx 基本一致
5、安装配置 redis
sudo yum install redis -y
Redis 配置主要包括设置持久化选项、网络配置、安全性设置等。以下是一个基本的配置示例:
# redis.conf
port 6379
bind 127.0.0.1
protected-mode yes
requirepass "yourpassword"
4、白名单实现
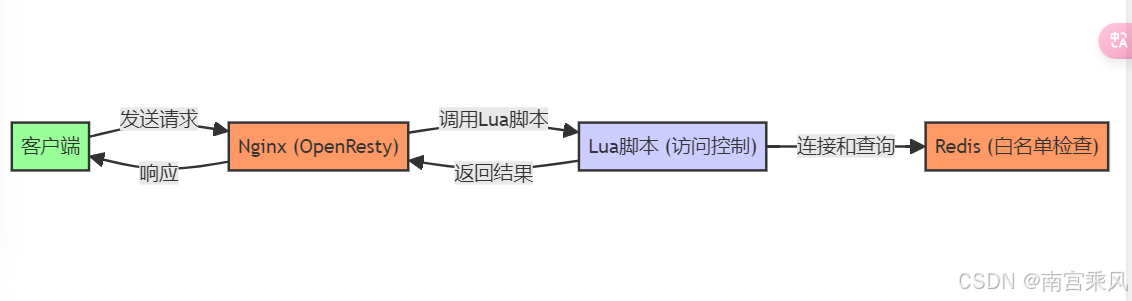
图例说明:
- 客户端:发送 HTTP 请求的用户或应用。
- Nginx (OpenResty):处理和管理 HTTP 请求,执行 Lua 脚本进行访问控制。
- Lua 脚本:在 Nginx 中运行,负责从 Redis 获取白名单并进行 IP 检查。
- Redis:存储白名单数据,用于快速查询。
交互流程:
- 客户端发送请求到 Nginx。
- Nginx 调用 Lua 脚本进行访问控制。
- Lua 脚本连接 Redis,并查询 IP 是否在白名单中。
- Lua 脚本返回查询结果给 Nginx。
- Nginx 根据结果决定是否允许请求,并返回响应给客户端
定义白名单的作用与重要性
白名单是一种安全策略,用于定义一组被信任的 IP 地址或实体,它们被允许访问特定的资源或服务。在 Web 应用中,白名单的作用尤为显著:
- 安全性增强:限制访问权限,仅允许特定的 IP 地址访问敏感资源。
- 防止滥用:减少恶意用户或爬虫对服务的滥用。
- 流量管理:通过控制访问源,更有效地管理网络流量。
通过 OpenResty Lua 脚本实现白名单逻辑
在 OpenResty 中,我们可以使用 Lua 脚本来实现白名单逻辑。Lua 脚本可以在 Nginx 的配置文件中直接编写,或者存储在外部文件中,并在配置文件中引用。
Lua 脚本实现步骤:
- 定义白名单:在 Redis 中存储白名单 IP 地址。
- 访问控制:在 Nginx 配置中使用
access_by_lua_block或access_by_lua_file指令调用 Lua 脚本。 - 脚本逻辑:检查请求的 IP 地址是否在白名单中,如果不在,则拒绝访问。
案例演示
jenkins.ownit.top.conf
这个是 nginx 的配置文件
最主要内容:access_by_lua_file /opt/nginx/lua_script/white.lua;
upstream jenkins-uat {
server 192.168.102.20:91;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name jenkins.ownit.top;
#白名单 或者 黑名单
#include /opt/nginx/whitelist/corporation.conf;
location / {
rewrite ^/(.*)$ https://$host/$1 permanent;
}
access_log /www/wwwlogs/dns.ownit.top.log;
error_log /www/wwwlogs/dns.ownit.top.error.log;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name jenkins.ownit.top;
#白名单 或者 黑名单
#include /opt/nginx/whitelist/corporation.conf;
#ssl on;
ssl_certificate /opt/nginx/ssl/ownit.top.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /opt/nginx/ssl/ownit.top.key;
include ssl.conf;
location / {
access_by_lua_file /opt/nginx/lua_script/white.lua; # nginx的lua脚本
proxy_pass http://jenkins-uat;
include https_proxy.conf;
}
access_log /www/wwwlogs/dns.ownit.top.log;
error_log /www/wwwlogs/dns.ownit.top.error.log;
}
white.lua文件
通过使用 Lua 脚本,在接收到 HTTP 请求时检查请求的 IP 地址是否在 Redis 存储的白名单中。如果 IP 不在白名单中,则拒绝访问。
思路
- 获取客户端 IP 和请求路径:在 Lua 脚本中获取客户端的 IP 地址和请求路径。
- 连接 Redis:使用
resty.redis模块连接 Redis 数据库。 - 权限校验:对连接的 Redis 进行认证。
- 检查 IP 是否在白名单中:从 Redis 中检查 IP 是否存在于白名单集合中。
- 返回结果:如果 IP 在白名单中,允许访问;否则,返回 403 Forbidden 状态码,拒绝访问。
- 释放 Redis 连接:将 Redis 连接返回到连接池中,以便复用。
-- 获取客户端IP和请求路径
local client_ip = ngx.var.remote_addr
local path = ngx.var.uri
-- Redis相关配置
local redis_key_white_list = "map_request_white_list"
-- 连接Redis
local redis = require "resty.redis"
local red = redis:new()
red:set_timeout(1000) -- 设置超时(毫秒)
local ok, err = red:connect("127.0.0.1", 6379)
if not ok then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "Redis连接失败: ", err)
return ngx.exit(500)
end
-- 权限校验
local res, err = red:auth("123456")
if not res then
ngx.say("failed to authenticate: ", err)
return
end
-- 检查IP是否在白名单中
local is_in_whitelist, err = red:sismember(redis_key_white_list, client_ip)
if is_in_whitelist == 1 then
ngx.log(ngx.INFO, "IP在白名单中: ", client_ip)
else
ngx.status = ngx.HTTP_FORBIDDEN
ngx.say("Access Denied")
return ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_FORBIDDEN)
end
-- 返还redis连接到连接池
local ok, err = red:set_keepalive(10000, 100)
if not ok then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "设置keepalive失败: ", err)
end
详细解释
-
获取客户端 IP 和请求路径
local client_ip = ngx.var.remote_addr local path = ngx.var.uri这两行代码从 Nginx 变量中获取客户端的 IP 地址和请求路径,
client_ip用于后续的白名单检查。 -
Redis 相关配置
local redis_key_white_list = "map_request_white_list"定义存储白名单的 Redis 键。
-
连接 Redis
local redis = require "resty.redis" local red = redis:new() red:set_timeout(1000) -- 设置超时(毫秒) local ok, err = red:connect("127.0.0.1", 6379) if not ok then ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "Redis连接失败: ", err) return ngx.exit(500) end使用
resty.redis模块创建 Redis 连接对象,并设置连接超时时间。尝试连接到 Redis 服务器,如果连接失败,记录错误日志并返回 500 错误。 -
权限校验
local res, err = red:auth("123456")
if not res then
ngx.say("failed to authenticate: ", err)
return
end
对 Redis 进行认证,如果认证失败,输出错误信息并停止执行。
- 检查 IP 是否在白名单中
local is_in_whitelist, err = red:sismember(redis_key_white_list, client_ip)
if is_in_whitelist == 1 then
ngx.log(ngx.INFO, "IP在白名单中: ", client_ip)
else
ngx.status = ngx.HTTP_FORBIDDEN
ngx.say("Access Denied")
return ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_FORBIDDEN)
end
使用SISMEMBER命令检查 IP 是否在 Redis 的白名单集合中。如果 IP 在白名单中,记录信息日志;否则,返回 403 Forbidden 状态码并拒绝访问。
- 释放 Redis 连接
local ok, err = red:set_keepalive(10000, 100)
if not ok then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "设置keepalive失败: ", err)
end
将 Redis 连接返回到连接池中,以便后续请求复用该连接。如果设置失败,记录错误日志。
在 Nginx 中配置 Lua 脚本
在 Nginx 的location配置中,使用access_by_lua_file指令来调用上述 Lua 脚本:
nginx复制代码http {
```lua
http {
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
location / {
access_by_lua_file /opt/nginx/lua_script/white.lua;
proxy_pass http://backend;
}
}
}
上述配置在接收到 HTTP 请求时,会首先执行/opt/nginx/lua_script/white.lua脚本进行白名单检查。如果通过检查,则继续将请求转发到后端服务器。
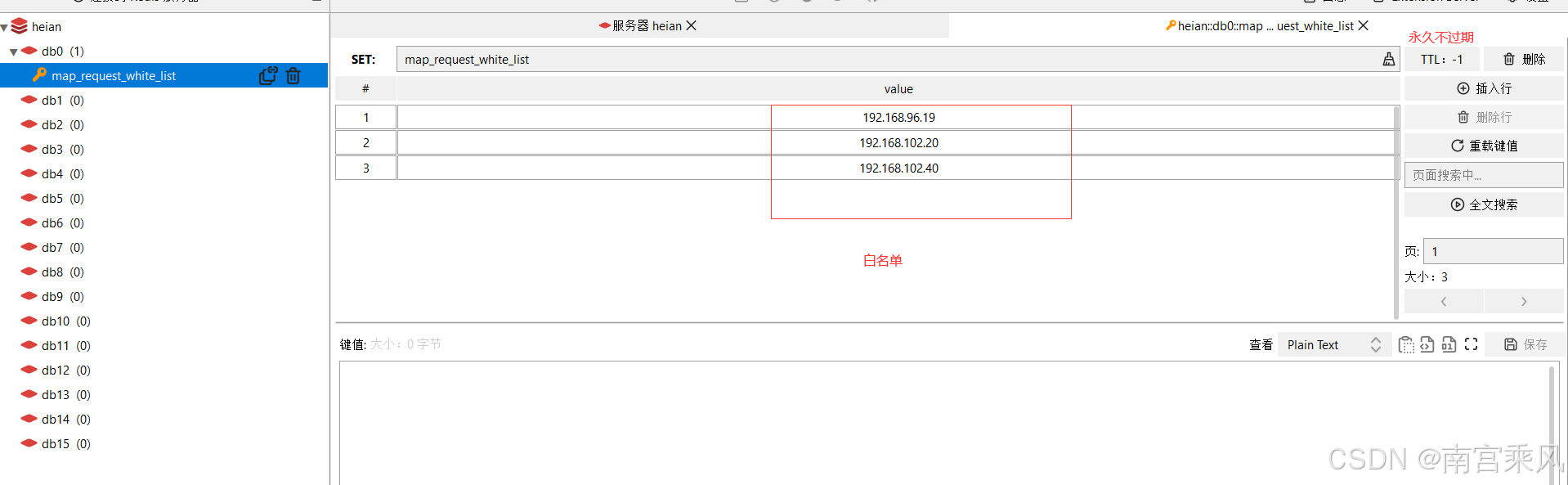
成功访问:
禁止访问:
5、黑名单实现
黑名单的作用与场景
黑名单是一种网络安全机制,用于识别并阻止恶意 IP 地址对服务器资源的访问。它在多种场景中发挥着重要作用:
- 防止恶意攻击:通过封禁已知的攻击者 IP,减少服务器遭受的恶意攻击。
- 打击爬虫滥用:限制爬虫对网站资源的过度访问,保护数据不被滥用。
- 减轻服务器负载:通过限制特定 IP 的访问频率,减轻服务器压力,提高服务稳定性。
- DDoS 防御:快速响应 DDoS 攻击,封禁攻击源 IP,保护服务可用性。
使用 Lua 脚本与 Redis 实现动态 IP 封禁
OpenResty 结合 Redis 可以实现一个高效的动态 IP 封禁系统。以下是实现的关键步骤:
- 环境配置:确保 Nginx OpenResty 和 Redis 环境准备就绪。
- Lua 脚本编写:编写 Lua 脚本来动态查询和更新 Redis 中的黑名单状态。
- Nginx 配置整合:在 Nginx 配置文件中集成 Lua 脚本,实现访问控制。

案例演示
通过使用 Lua 脚本,在接收到 HTTP 请求时检查请求的 IP 地址是否在黑名单中,或控制 IP 的访问频率,并进行相应的处理。
思路
- 获取客户端 IP:在 Lua 脚本中获取客户端的 IP 地址。
- 连接 Redis:使用
resty.redis模块连接 Redis 数据库。 - 权限校验:对连接的 Redis 进行认证。
- 检查 IP 是否在黑名单中:从 Redis 中检查 IP 是否存在于黑名单集合中。
- 访问频次控制:对每个 IP 的访问频次进行限制,如果超过指定的频次,则将 IP 加入黑名单。
- 返回结果:如果 IP 在黑名单中,返回 403 Forbidden 状态码,拒绝访问;否则,允许请求继续。
Nginx 配置文件
upstream jms-uat {
server 192.168.82.105:81;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name jms.ownit.top;
# 白名单 或者 黑名单
# include /opt/nginx/whitelist/corporation.conf;
rewrite ^/(.*)$ https://$host/$1 permanent;
access_log /www/wwwlogs/dns.ownit.top.log;
error_log /www/wwwlogs/dns.ownit.top.error.log;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name jms.ownit.top;
# 白名单 或者 黑名单
# include /opt/nginx/whitelist/corporation.conf;
ssl_certificate /opt/nginx/ssl/ownit.top.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /opt/nginx/ssl/ownit.top.key;
include ssl.conf;
location = /core/auth/login/ {
access_by_lua_file /opt/nginx/lua_script/login.lua;
proxy_pass http://jms-uat;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
}
location / {
if ($request_uri !~ \.(html|htm|jpg|png|ico|js|css)$) {
access_by_lua_file /opt/nginx/lua_script/rule.lua;
}
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_pass http://jms-uat;
include https_proxy.conf;
client_max_body_size 0;
}
access_log /www/wwwlogs/dns.ownit.top.log;
error_log /www/wwwlogs/dns.ownit.top.error.log;
}
location = /core/auth/login/
location = /core/auth/login/ {
access_by_lua_file /opt/nginx/lua_script/login.lua;
proxy_pass http://jms-uat;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
}
解释
location = /core/auth/login/:- 这是一个精确匹配的
location块,仅对请求路径严格等于/core/auth/login/的请求生效。
- 这是一个精确匹配的
access_by_lua_file /opt/nginx/lua_script/login.lua;:- 使用 OpenResty 的 Lua 模块,指定在访问控制阶段执行
/opt/nginx/lua_script/login.lua脚本。这个脚本通常用于执行认证、权限检查或其他预处理逻辑。
- 使用 OpenResty 的 Lua 模块,指定在访问控制阶段执行
proxy_pass http://jms-uat;:- 将匹配到的请求代理到上游服务器
http://jms-uat。
- 将匹配到的请求代理到上游服务器
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;:- 设置
Upgrade请求头,支持 WebSocket 等协议升级。$http_upgrade变量包含原始请求中的Upgrade头字段的值。
- 设置
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";:- 设置
Connection请求头为upgrade,通常与Upgrade头一起使用,以确保连接升级。
- 设置
location /
location / {
# 如果该location 下存在静态资源文件可以做一个判断
if ($request_uri !~ \.(html|htm|jpg|png|ico|js|css)$) {
access_by_lua_file /opt/nginx/lua_script/rule.lua; 加上了这条配置,则会根据 rule.lua 的规则进行限流
}
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_pass http://jms-uat;
include https_proxy.conf;
client_max_body_size 0;
}
解释
location /:- 这是一个通配符匹配的
location块,表示所有路径的请求都会匹配到这个块,除非有其他更精确的匹配块。
- 这是一个通配符匹配的
if ($request_uri !~ \.(html|htm|jpg|png|ico|js|css)$):- 使用
if指令对请求路径进行检查。仅在请求路径不匹配指定的静态资源文件扩展名(如.html,.htm,.jpg,.png,.ico,.js,.css)时,执行后续的 Lua 脚本。这种检查有助于将动态资源与静态资源区分开来。
- 使用
access_by_lua_file /opt/nginx/lua_script/rule.lua;:- 使用 OpenResty 的 Lua 模块,指定在访问控制阶段执行
/opt/nginx/lua_script/rule.lua脚本。这个脚本通常用于实现限流、防火墙或其他动态访问控制逻辑。
- 使用 OpenResty 的 Lua 模块,指定在访问控制阶段执行
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;:- 设置
Upgrade请求头,支持 WebSocket 等协议升级。$http_upgrade变量包含原始请求中的Upgrade头字段的值。
- 设置
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";:- 设置
Connection请求头为upgrade,通常与Upgrade头一起使用,以确保连接升级。
- 设置
proxy_pass http://jms-uat;:- 将匹配到的请求代理到上游服务器
http://jms-uat。
- 将匹配到的请求代理到上游服务器
include https_proxy.conf;:- 包含额外的配置文件
https_proxy.conf,该文件可能包含 HTTPS 代理相关的其他配置项。
- 包含额外的配置文件
client_max_body_size 0;:- 设置客户端请求体的最大大小为 0,表示不限制请求体的大小。
这两个 location 块主要用于处理不同路径的请求,并在访问控制阶段使用 Lua 脚本进行相应的逻辑处理。精确匹配的 / core/auth/login / 路径专用于特定的认证或预处理,而通配符匹配的 / 路径则处理所有其他请求,并进行动态访问控制逻辑。两者共同确保了 Nginx 服务器的灵活性和安全性。
Lua 脚本 (rule.lua)
-- 连接池超时回收毫秒
local pool_max_idle_time = 10000
-- 连接池大小
local pool_size = 100
-- redis 连接超时时间
local redis_connection_timeout = 100
-- redis host
local redis_host = "192.168.102.20"
-- redis port
local redis_port = "6379"
-- redis auth
local redis_auth = "123456"
-- 封禁IP时间(秒)
local ip_block_time = 120
-- 指定ip访问频率时间段(秒)
local ip_time_out = 10
-- 指定ip访问频率计数最大值(次)
local ip_max_count = 60
-- 错误日志记录
local function errlog(msg, ex)
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, msg, ex)
end
-- 释放连接池
local function close_redis(red)
if not red then
return
end
local ok, err = red:set_keepalive(pool_max_idle_time, pool_size)
if not ok then
ngx.say("redis connct err:", err)
return red:close()
end
end
-- 连接redis
local redis = require "resty.redis"
local client = redis:new()
local ok, err = client:connect(redis_host, redis_port)
-- 连接失败返回服务器错误
if not ok then
return
end
-- 设置超时时间
client:set_timeout(redis_connection_timeout)
-- 优化验证密码操作
local connCount, err = client:get_reused_times()
-- 新建连接,需要认证密码
if 0 == connCount then
local ok, err = client:auth(redis_auth)
if not ok then
errlog("failed to auth: ", err)
return
end
elseif err then
errlog("failed to get reused times: ", err)
return
end
-- 获取请求ip
local function getIp()
local clientIP = ngx.req.get_headers()["X-Real-IP"]
if clientIP == nil then
clientIP = ngx.req.get_headers()["x_forwarded_for"]
end
if clientIP == nil then
clientIP = ngx.var.remote_addr
end
return clientIP
end
local clientIp = getIp()
local incrKey = "limit:all:count:" .. clientIp
local blockKey = "limit:all:block:" .. clientIp
-- 查询ip是否被禁止访问,如果存在则返回403错误代码
local is_block, err = client:get(blockKey)
if tonumber(is_block) == 1 then
ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_FORBIDDEN)
close_redis(client)
end
local ip_count, err = client:incr(incrKey)
if tonumber(ip_count) == 1 then
client:expire(incrKey, ip_time_out)
end
-- 如果超过单位时间限制的访问次数,则添加限制访问标识,限制时间为ip_block_time
if tonumber(ip_count) > tonumber(ip_max_count) then
client:set(blockKey, 1)
client:expire(blockKey, ip_block_time)
end
close_redis(client)
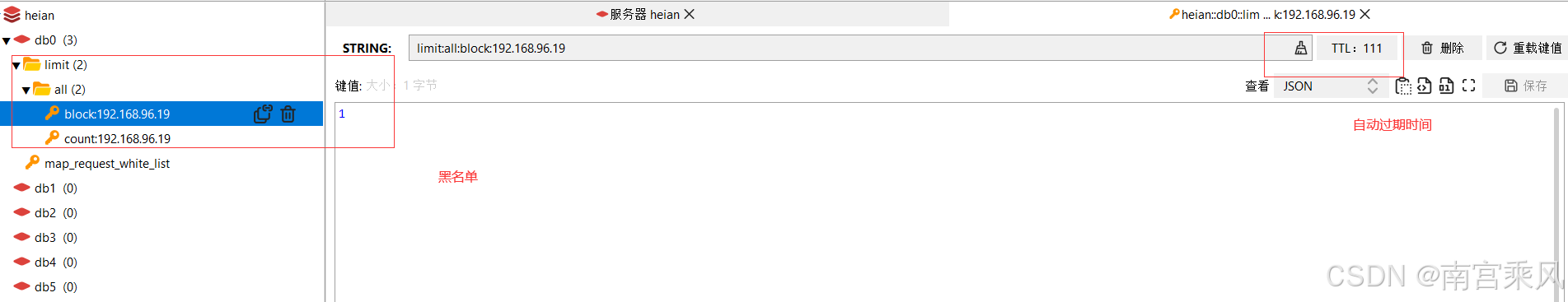
成功访问:

失败访问:
